Handling Bedbugs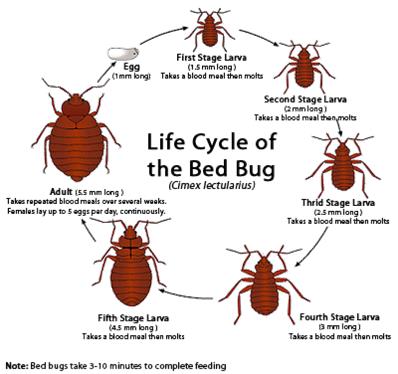
A Bit About Bedbugs
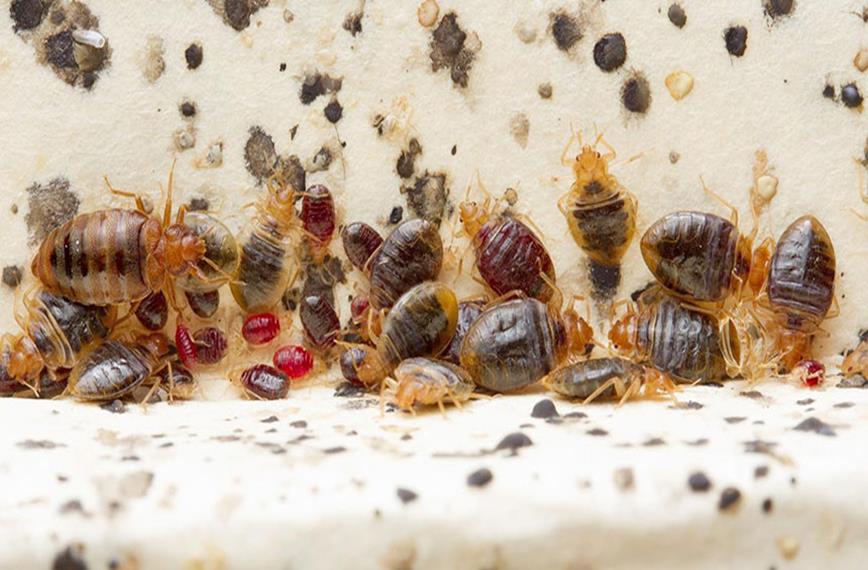
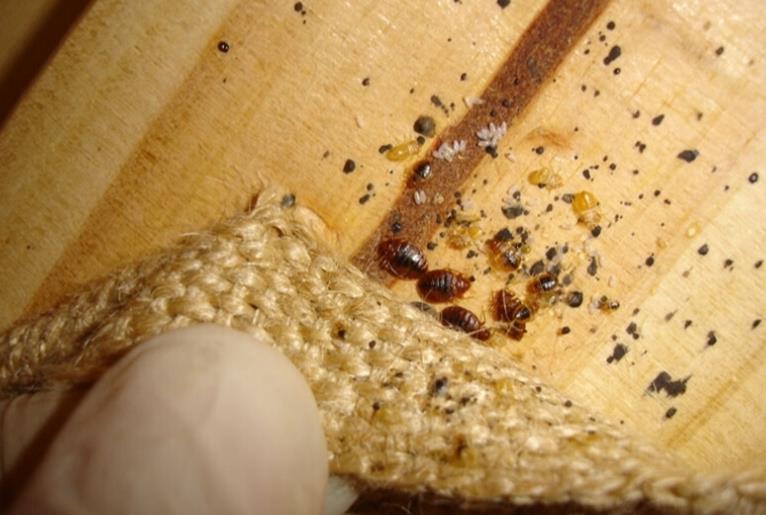
Bedbugs are small, flat, oval shaped, non-flying insects that belong to the family Cimicidae, which includes at least two species that prefer to bite, and feed from, people. Adult bedbugs typically reach 5mm -7mm in length and are a reddish brown color. Nymphs (juveniles) can be as small as 1.5mm and are typically clear. Bedbugs are more active at night, feeding on blood every 5 to 10 days. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), it can take up to 14 days for bites to appear and most bites are not noticeable until after a skin reaction has occurred. Bedbug bites can look very similar to bites from other insects like mosquitos and fleas. People also have widely varying reactions to bedbug bites. Some people have little visible reaction to the insects' nibbling — they don't develop lesions or bumps or pustules at all. The bites themselves don't usually pose any major health risk since bedbugs are not known to spread diseases, but an allergic reaction to the bites may require medical attention. The lifespan of a bed bug most commonly ranges from four to six months. But some bedbugs may live up to a year under cool conditions! Detecting Infestations Bedbugs may enter your home undetected through luggage, clothing, used beds and couches, and other items. Their flattened bodies make it possible for them to fit into very tiny spaces. Bedbugs do not have nests like ants or bees, but tend to live in groups in hiding places such as mattresses, box springs, bed frames, and headboards where they have easy access to people to bite in the night. Temperatures between 70F - 80F are most favorable for bedbugs, allowing them to develop into adults most rapidly and then go on to produce up to three generations per year. A female bedbug can lay hundreds of eggs during her life span! The creatures don't discriminate between dirty and clean either, which means even luxury hotels can be susceptible to bedbugs. The most at-risk places tend to be crowded lodgings with high occupant turnover, such as dorms, apartment complexes, hotels, and homeless shelters. Getting rid of clutter may help to reduce the number of hiding places for bedbugs, but according to the CDC, the best way to prevent bedbugs is regular inspection for the signs of an infestation - visible bedbugs in bedding, rust-colored spots on bedding, a coriander like odor, or bedbug shells/molted skins are all indicators you may have bedbugs. How to Handle Infestations Getting rid of bedbugs is not an easy process, and most cases of bedbug infestation will require treatment by a pest control expert. Bedbugs can survive for several months without feeding, so they may persist even in unoccupied rooms. Getting rid of bedbugs begins with cleaning up the places where bedbugs live. This should include the following:
Download our brochure. |


